之前讲工作流的启动,源头是t_ds_command表,这篇笔记讲讲该表数据是如何写入的,也就是 Crontab 的生效过程。
1. quartz
简单的 crontab 实现方式很多,java.util.Timer、spring @Scheduled、akka scheduler etc.。 quartz1也是一个调度框架,可以集成在 java 程序里,好处是持久化和分布式。
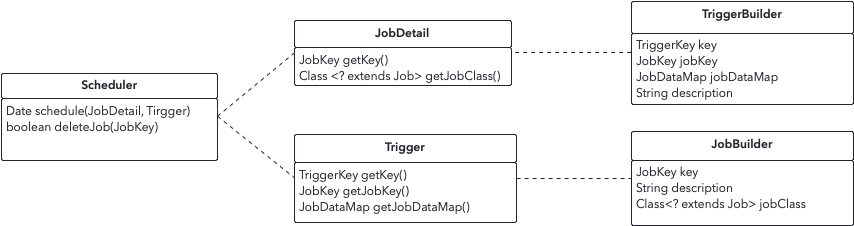
我觉得 quartz 里最重要的概念有三个:
- JobDetail: 用户继承该基类实现自己的任务类,执行具体任务
- Trigger: 任务触发器,比如一次性触发、Crontab 触发等
- Scheduler: 调度器,接收 JobDetail,按照 Trigger 调度
JobBuilder、TiggerBuilder、JobKey、TriggerKey等都是伴生的名词,如图所示:
Date scheduleJob(JobDetail jobDetail, Trigger trigger)添加新的作业及触发器,方法接收两个参数:
JobDetail: 保存了job唯一名、任务类、job额外属性等Trigger: 保存了trigger唯一名、trigger类型、trigger时间等
代码示例比较简单,我放到了Bigdata-Systems2
定义了两个任务,进程启动后会开始调度:
2023-11-18 23:50:20.016 [DolphinScheduler_Worker-1] INFO cn.izualzhy.QuartzJob - start taskName:quartz-job1 ...
2023-11-18 23:50:20.016 [DolphinScheduler_Worker-1] INFO cn.izualzhy.QuartzJob - stop taskName:quartz-job1 ...
2023-11-18 23:50:20.035 [DolphinScheduler_Worker-2] INFO cn.izualzhy.QuartzJob - start taskName:quartz-job2 ...
2023-11-18 23:50:20.035 [DolphinScheduler_Worker-2] INFO cn.izualzhy.QuartzJob - stop taskName:quartz-job2 ...
2. 持久化与分布式
持久化是我们在生产环境要考虑的第一个问题,quartz 里相关的配置:org.quartz.jobStore.class,可以是RAMJobStore,也可以是JobStoreTX LocalDataSourceJobStore,后者支持job、trigger持久化到数据库。
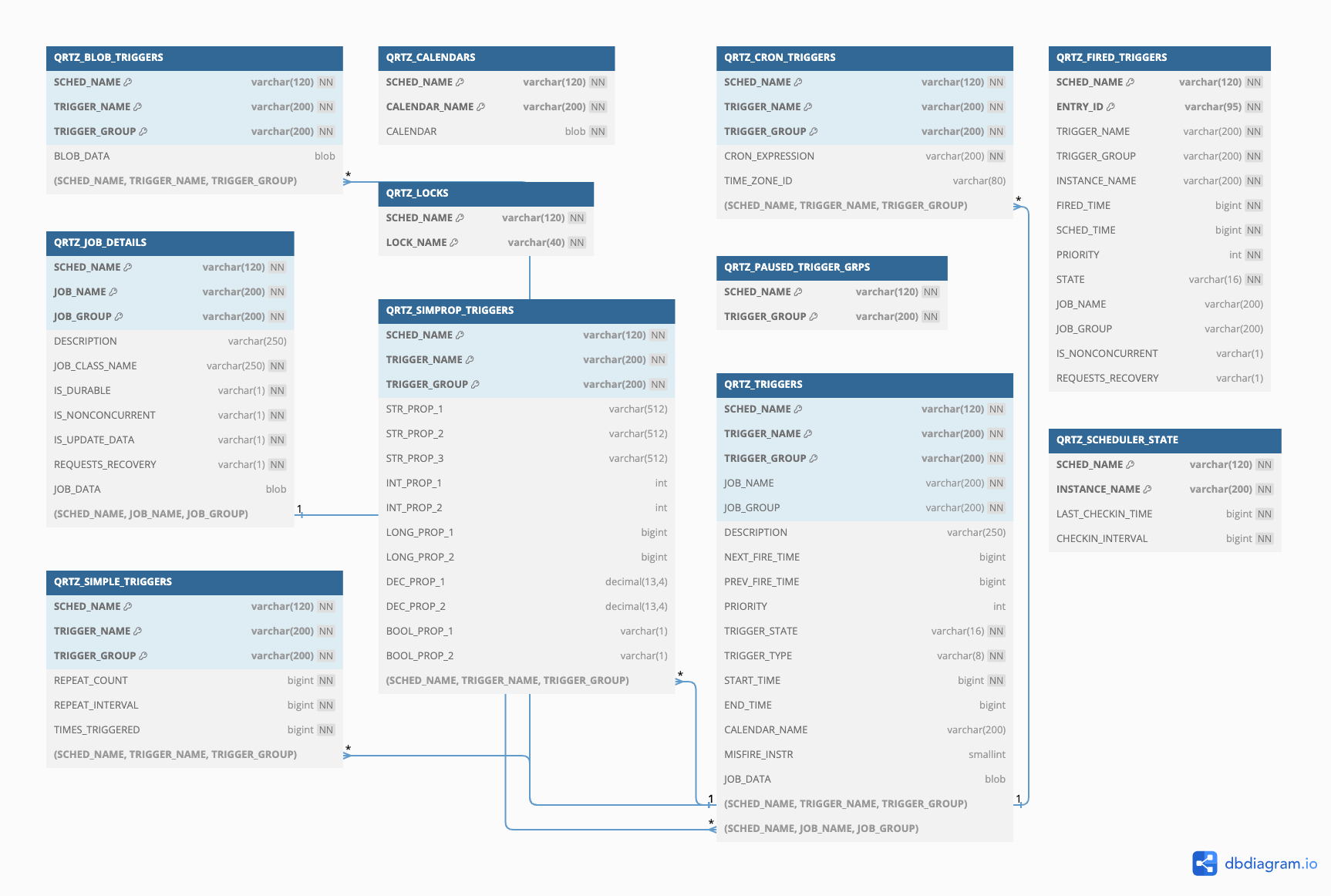
用户层面关注比较多的几个表:
- QRTZ_TRIGGERS: 基础 Trigger 信息,上次触发时间、下次触发时间、trigger 状态等
- QRTZ_XXX_TRIGGERS: 存储CronTrigger、SimpleTrigger、DailyTimeIntervalTrigger、CalendarIntervalTrigger、自定义Trigger等信息
- QRTZ_JOB_DETAILS: Job名、任务类、任务附加信息等
常见的 trigger 状态有:
| 状态 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| WAITING | the normal state of a trigger, waiting for its fire time to arrive and be acquired for firing by a scheduler. |
| PAUSED | means that one of the scheduler.pauseXXX() methods was used. The trigger is not eligible for being fired until it is resumed. |
| ACQUIRED | a scheduler node has identified this trigger as the next trigger it will fire - may still be waiting for its fire time to arrive. After it fires the trigger will be updated (per its repeat settings, if any) and placed back into the WAITING state (or be deleted if it does not repeat again). |
| BLOCKED | the trigger is prevented from being fired because it relates to a StatefulJob that is already executing. When the statefuljob completes its execution, all triggers relating to that job will return to the WAITING state. |
持久化相关代码实现可以参考JobStoreSupport::storeJobAndTrigger
quartz 同样支持集群模式,例子2多进程的情况下,任务到了启动时间,由且只由单个进程启动。
分布式相关代码实现可以参考QuartzSchedulerThread::run、JobStore::acquireNextTriggers,核心实现在:
public abstract class DBSemaphore implements Semaphore, Constants,
StdJDBCConstants, TablePrefixAware {
public boolean obtainLock(Connection conn, String lockName) {
// SELECT * FROM QRTZ_LOCKS WHERE SCHED_NAME = '?' AND LOCK_NAME = ? FOR UPDATE
}
}
使用了排他锁。
3. dolphin应用
3.1. QuartzExecutorImpl
页面上对定时管理的操作会调用到class QuartzExecutorImpl,其中addJob里负责更新工作流及其定时管理:
public class QuartzExecutorImpl implements QuartzExecutor {
@Override
public void addJob(Class<? extends Job> clazz, int projectId, final Schedule schedule) {
String jobName = this.buildJobName(schedule.getId());
String jobGroupName = this.buildJobGroupName(projectId);
Map<String, Object> jobDataMap = this.buildDataMap(projectId, schedule);
// ...
lock.writeLock().lock();
try {
JobKey jobKey = new JobKey(jobName, jobGroupName);
JobDetail jobDetail;
//add a task (if this task already exists, return this task directly)
if (scheduler.checkExists(jobKey)) {
jobDetail = scheduler.getJobDetail(jobKey);
jobDetail.getJobDataMap().putAll(jobDataMap);
} else {
jobDetail = newJob(clazz).withIdentity(jobKey).build();
jobDetail.getJobDataMap().putAll(jobDataMap);
scheduler.addJob(jobDetail, false, true);
}
TriggerKey triggerKey = new TriggerKey(jobName, jobGroupName);
/*
* Instructs the Scheduler that upon a mis-fire
* situation, the CronTrigger wants to have it's
* next-fire-time updated to the next time in the schedule after the
* current time (taking into account any associated Calendar),
* but it does not want to be fired now.
*/
CronTrigger cronTrigger = newTrigger()
.withIdentity(triggerKey)
.startAt(startDate)
.endAt(endDate)
.withSchedule(
cronSchedule(cronExpression)
.withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing()
.inTimeZone(DateUtils.getTimezone(timezoneId))
)
.forJob(jobDetail).build();
if (scheduler.checkExists(triggerKey)) {
// updateProcessInstance scheduler trigger when scheduler cycle changes
CronTrigger oldCronTrigger = (CronTrigger) scheduler.getTrigger(triggerKey);
String oldCronExpression = oldCronTrigger.getCronExpression();
if (!StringUtils.equalsIgnoreCase(cronExpression, oldCronExpression)) {
// reschedule job trigger
scheduler.rescheduleJob(triggerKey, cronTrigger);
}
} else {
scheduler.scheduleJob(cronTrigger);
}
...
}
核心代码都在上面了,注意几点:
- 第一个参数是用户任务类,传入了
ProcessScheduleJob.class - CronTrigger 里指定了
startDate、endDate、withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing - jobName 使用了
schedule.getId(),也就是t_ds_schedules.id,这是 dolphin 自身的表和 quartz 表的关联点
3.2. ProcessScheduleJob
ProcessScheduleJob继承自QuartzJobBean,重载了executeInternal方法。我们在工作流里看到的调度时间,实际上就是 quartz 里的getScheduledFireTime。
public class ProcessScheduleJob extends QuartzJobBean {
protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext context) {
JobDataMap dataMap = context.getJobDetail().getJobDataMap();
int projectId = dataMap.getInt(Constants.PROJECT_ID);
int scheduleId = dataMap.getInt(Constants.SCHEDULE_ID);
Date scheduledFireTime = context.getScheduledFireTime();
Date fireTime = context.getFireTime();
// query schedule
Schedule schedule = processService.querySchedule(scheduleId);
...
ProcessDefinition processDefinition = processService.findProcessDefinitionByCode(schedule.getProcessDefinitionCode());
...
Command command = new Command();
command.setScheduleTime(scheduledFireTime);
...
processService.createCommand(command);
}
}
4. misfire
第三节里提到了withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing,先说下 misfire 的背景:
crontab 到了触发的时间点,可能正常执行,也可能由于某些原因不能执行,比如 schedule 全部宕机了、线程打满导致实际调度比预期时间晚了很久等。
不同场景就会有不同的选择:
- 离线数仓调度:由于必须要产出当天的分区,因此需要能够保证执行
- 实时数仓构建:由于调度频率高,容错性强,因此可以跳过执行
- 业务场景:不同场景下需求不同,如果允许,要考虑“贪吃蛇”的现象
quartz 针对上述需求,使用了 misfire 的概念(到达 crontab 时间时启动任务称为fire🚀,没有则称为 misfire)
- 多久没有触发,则认为 misfire,通过 org.quartz.jobStore.misfireThreshold 配置。
- 触发后的行为,在 trigger 里配置,称为 misfire 策略。不同 trigger 类型可配置的不同
比如 CronTrigger,可以配置的 misfire 策略有:
public class CronScheduleBuilder extends ScheduleBuilder<CronTrigger> {
public CronScheduleBuilder withMisfireHandlingInstructionIgnoreMisfires() {
misfireInstruction = Trigger.MISFIRE_INSTRUCTION_IGNORE_MISFIRE_POLICY;
return this;
}
public CronScheduleBuilder withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing() {
misfireInstruction = CronTrigger.MISFIRE_INSTRUCTION_DO_NOTHING;
return this;
}
public CronScheduleBuilder withMisfireHandlingInstructionFireAndProceed() {
misfireInstruction = CronTrigger.MISFIRE_INSTRUCTION_FIRE_ONCE_NOW;
return this;
}
}
各策略说明:
| misfire instruction | 策略效果 |
|---|---|
| withMisfireHandlingInstructionIgnoreMisfires (MISFIRE_INSTRUCTION_IGNORE_MISFIRE_POLICY) |
立即补全 All misfired executions are immediately executed, then the trigger runs back on schedule. Example scenario: the executions scheduled at 9 and 10 AM are executed immediately. The next scheduled execution (at 11 AM) runs on time. |
| withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing (withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing) |
立即补全最早的一次 Immediately executes first misfired execution and discards other (i.e. all misfired executions are merged together). Then back to schedule. No matter how many trigger executions were missed, only single immediate execution is performed. Example scenario: the executions scheduled at 9 and 10 AM are merged and executed only once (in other words: the execution scheduled at 10 AM is discarded). The next scheduled execution (at 11 AM) runs on time. |
| withMisfireHandlingInstructionFireAndProceed (CronTrigger.MISFIRE_INSTRUCTION_FIRE_ONCE_NOW) |
忽略所有 All misfired executions are discarded, the scheduler simply waits for next scheduled time. Example scenario: the executions scheduled at 9 and 10 AM are discarded, so basically nothing happens. The next scheduled execution (at 11 AM) runs on time. |
其他类型的 trigger,例如class SimpleScheduleBuilder也都有自己的 misfire 策略4.
dolphin 里默认的行为是CronScheduleBuilder.withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing.
5. 漏调度:missed their scheduled fire-time
使用 dolphin 的同学,对这个日志应该不陌生:
2023-11-19 22:14:54.049 [...] INFO ... - Handling 1 trigger(s) that missed their scheduled fire-time.
针对第1节的例子,做以下改动:
- 调度线程修改为1:org.quartz.threadPool.threadCount: 1
- 任务执行时增加 sleep 15s
单线程调度执行,同时配置了org.quartz.jobStore.misfireThreshold: 3000.而 job-1 每 10s 调度一次,每次执行时间 15s,因此就会触发 job-1 的 misfire 策略withMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing
| 日志时间 | 日志行为 | fire-time | next-fire-time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22:26:40 | 执行job-1 | 22:26:40 | 22:26:50 |
| 22:26:55 | 执行job-1完成 打印日志 Handling 1 trigger(s) that missed their scheduled fire-time |
||
| 22:27:00 | 执行job-1 | 22:27:00 | 22:27:10 |
| 22:27:15 | 执行job-1完成 打印日志 Handling 1 trigger(s) that missed their scheduled fire-time |
也就是中间应该有的一次 trigger 被 misfire 了,在线上环境,就是一次漏调度的case,需要重视
5.1. 源码相关:recoverMisfiredJobs
再次回到这篇笔记里提到多次的JobStore: 线程方法manage里会调用recoverMisfiredJobs:
public abstract class JobStoreSupport implements JobStore, Constants {
public void run() {
while (!shutdown) {
RecoverMisfiredJobsResult recoverMisfiredJobsResult = manage();
...
Thread.sleep(timeToSleep);
}
}
protected RecoverMisfiredJobsResult recoverMisfiredJobs(
Connection conn, boolean recovering)
throws JobPersistenceException, SQLException {
// If recovering, we want to handle all of the misfired
// triggers right away.
int maxMisfiresToHandleAtATime =
(recovering) ? -1 : getMaxMisfiresToHandleAtATime();
List<TriggerKey> misfiredTriggers = new LinkedList<TriggerKey>();
long earliestNewTime = Long.MAX_VALUE;
// We must still look for the MISFIRED state in case triggers were left
// in this state when upgrading to this version that does not support it.
boolean hasMoreMisfiredTriggers =
getDelegate().hasMisfiredTriggersInState(
conn, STATE_WAITING, getMisfireTime(),
maxMisfiresToHandleAtATime, misfiredTriggers);
if (hasMoreMisfiredTriggers) {
getLog().info(
"Handling the first " + misfiredTriggers.size() +
" triggers that missed their scheduled fire-time. " +
"More misfired triggers remain to be processed.");
} else if (misfiredTriggers.size() > 0) {
getLog().info(
"Handling " + misfiredTriggers.size() +
" trigger(s) that missed their scheduled fire-time.");
} else {
getLog().debug(
"Found 0 triggers that missed their scheduled fire-time.");
return RecoverMisfiredJobsResult.NO_OP;
}
...
}
}
recoverMisfiredJobs方法检测是否有漏调度的任务,如果有,就打印上述日志。检测是通过 SQL 实现的:
-- SELECT_HAS_MISFIRED_TRIGGERS_IN_STATE
SELECT TRIGGER_NAME, TRIGGER_GROUP FROM {0}TRIGGERS
WHERE SCHED_NAME = {1} AND NOT (MISFIRE_INSTR = -1)
AND NEXT_FIRE_TIME < ? AND TRIGGER_STATE = ?
ORDER BY NEXT_FIRE_TIME ASC, PRIORITY DESC
-- {0} -> QRTZ_
-- {1} -> "DolphinScheduler"
-- ? = ('WAITING', getMisfireTime())
getMisfireTime()即当前时间-misfireThreshold,上述代码简单总结就是:
NEXT_FIR_TIME表示任务预计下次调度的时间,如果时间已经过了NEXT_FIRE_TIME+threshold,而 trigger 还处于 WAITING 状态,那么就认为这个 trigger misfire 了
这也是 misfire 本来的定义。
5.2. 如何监控和解决
原因分析清楚了,如何解决?
我的经验无外乎是以下几点:
- 多进程提高并发
- 提高 quartz 调度线程提高并发
- 提高 quartz misfireThreshold 避免触发
如果还有问题,由于相关操作几乎全部集中在数据库,就需要考虑数据库的性能了,trigger 量级在几万的话,数据库一般都不会成为瓶颈
还有一点是如何监控,这是这两年工作比较痛的点,由于缺乏合理的晋升评价/项目复盘制度,大多数人选择救火而做不到提前扑灭问题。
我想到的方法是在日志里输出工作流实际fire时间 - 工作流预期fire的时间,如果这个值接近 misfireThreshold,就需要提前评估性能了。
6. 一定是漏调度么?
按照上面的源码分析,如果漏调度了,一定会打印missed their scheduled fire-time的日志。
那么如果打印了该日志,就一定表示漏调度了么?如果可以的话,那么这个日志应该是 P0 日志,可以帮我们预警漏调度的问题。
可惜答案是否定的,当我们新插入一条 trigger ,如果指定了 startDate,例如:
trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.withIdentity(triggerName, TRIGGER_GROUP_NAME)
.withSchedule(cronScheduleBuilder)
.startAt(Date.from(
LocalDate.of(2023, 11, 1)
.atStartOfDay(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()))
QRTZ_TRIGGERS 表里的记录:
| SCHED_NAME | TRIGGER_NAME | NEXT_FIRE_TIME | PREV_FIRE_TIME | START_TIME | MISFIRE_INSTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DolphinScheduler | trigger-1 | 1698804000000 | -1 | 1698768000000 | 2 |
也就是说初始化的NEXT_FIRE_TIME是基于startAt的,此时也就会触发一次missed their scheduled fire-time的日志了