DolphinScheduler 使用 Netty 作为网络框架,实现 Master Worker 模块间的 RPC 通信。这篇笔记介绍 DolphinScheduler 基础的网络模型,以及是如何使用 Netty 的。
1. Netty 简介
Netty 是 java 一款高性能的通信框架,使用上跟 C++ RPC 库很像,不像 akka 过于抽象和简洁。
Netty-Server 需要定义两个 NioEventLoopGroup 的线程组,一组用于接受 Client 的连接,一组用于 socket 的网络读写。通过 ServerBootStrap 辅助类,注册 handle 处理链,监听指定端口。
Netty-Client 需要定义一个 NioEventLoopGroup 线程组,通过 BootStrap 辅助类,注册 handle 处理链,连接指定端口。
handle 基本是一致的,通过实现 channelRead channelReadComplete channelActive exceptionCaught 等方法处理网络I/O事件。
2. DolphinScheduler 的网络通信模型
Master Worker 间的通信是通过 Netty 而非 Spring 实现的,Master 发送任务到 Worker,Worker 发送任务结果回 Master,因此两者在 RPC 上是对等的,都需要实现 RPC Server/Client.
底层复用一套代码。如图:
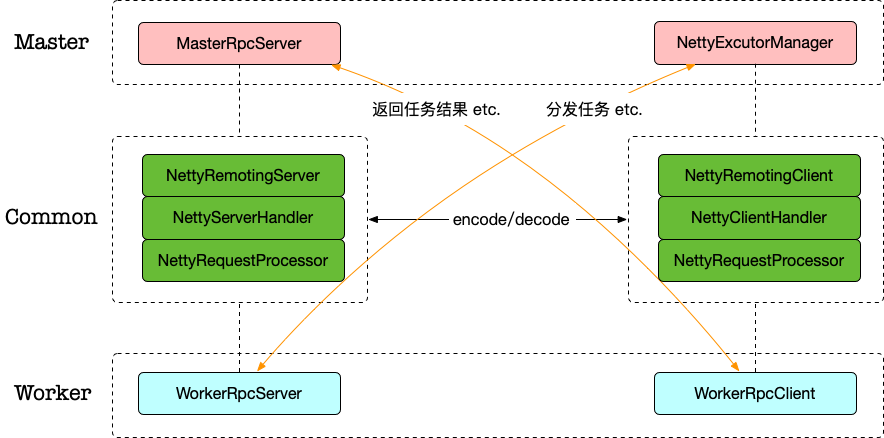
WorkerRpcClient跟MasterRpcServer通信:例如任务执行结果、任务KILL是否成功、任务拒绝等等NettyExeuctorManager跟WorkerRpcServer通信:例如分发任务、KILL任务、ACK等等
Commmon 部分是复用的代码:启动 Server/Client、注册 handler、统一的序列化/反序列化等.
RPC 一个典型的问题是如何根据消息体调用对应的本地方法,Master Worker 有各自关心的请求类型,例如 Master 接收任务执行、KILL、分发的结果,Worker 接收启动、停止任务的命令。
这些是通过注册不同的NettyRequestProcessor类型实现的,RPC 收到数据后先反序列化,根据反序列化的结果执行不同的NettyRequestProcessor子类处理。例如当 Worker 模块收到分发任务的消息时,就会调用TaskDispatchProcessor.process方法处理。
3. 序列化/反序列化
TCP 以流的方式传输,上层的应用协议需要对消息进行区分,以实现 TCP 的粘包/拆包。
常见的方式有 Google 的 Protobuf,这是一款非常高效、实用的序列化/反序列化框架,可以参考之前使用 protobuf + boost.asio 的笔记:如何基于protobuf实现一个极简版的RPC
DolphinScheduler 是通过自定义的NettyEncoder NettyDecoder实现的。Command对象序列化后的字节流:
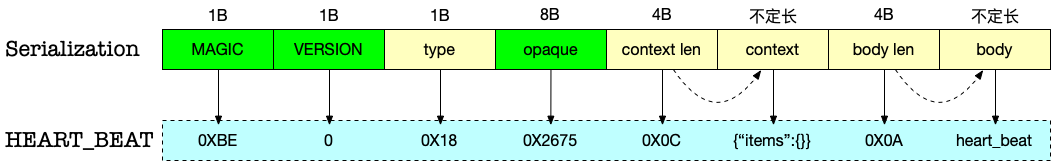
包含几部分:
- MAGIC: 魔数,dolphin 里用的是 0XBABE,实际只有低位字节有用。校验用,类似 leveldb sst 里的magic words
- VERSION: 版本,后续扩展备用
- type: 请求类型,对应
CommandType的定义,例如 TASK_DISPATCH_REQUEST、HEART_BEAT … - opaque: 自增ID
- context: 前 4Bytes 记录长度,按照记录的长度再写入 context,固定为 Map<String, String> json 序列化后的内容,用于存储额外信息。
- body: 前 4Bytes 记录长度,按照记录的长度再写入 body.这段 buf 存储了业务逻辑实现关注的消息内容,例如
TaskDispatchCommand
图里是一个心跳包发送的数据内容示例。
反序列化即字节流转为Command的过程,根据type调用不同的 processor 处理:
/**
* netty request processor
*/
public interface NettyRequestProcessor {
/**
* process logic
* @param channel channel
* @param command command
*/
void process(final Channel channel, final Command command);
}
4. NettyRemotingClient/Server
从前面的图里可以看到,Master Worker 都用到了NettyRemotingServer NettyRemotingClient对象,实现上就是使用 Netty 的标准流程:
// Server实现:EventLoopGroup、handle、bind 等
public class NettyRemotingServer {
public void start() {
this.serverBootstrap
.group(this.bossGroup, this.workGroup)
...
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
initNettyChannel(ch);
}
});
ChannelFuture future;
try {
future = serverBootstrap.bind(serverConfig.getListenPort()).sync();
...
private void initNettyChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast("encoder", new NettyEncoder())
.addLast("decoder", new NettyDecoder())
.addLast("server-idle-handle", new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, Constants.NETTY_SERVER_HEART_BEAT_TIME, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
.addLast("handler", serverHandler);
}
public void registerProcessor(final CommandType commandType, final NettyRequestProcessor processor, final ExecutorService executor) {
this.serverHandler.registerProcessor(commandType, processor, executor);
}
// Client实现:EventLoopGroup、handle、connect 等
public class NettyRemotingClient implements AutoCloseable {
private void start() {
this.bootstrap
.group(this.workerGroup)
...
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast("client-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(Constants.NETTY_CLIENT_HEART_BEAT_TIME, 0, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
.addLast(new NettyDecoder(), clientHandler, encoder);
}
});
public Channel createChannel(Host host, boolean isSync) {
ChannelFuture future;
try {
synchronized (bootstrap) {
future = bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host.getIp(), host.getPort()));
}
public void registerProcessor(final CommandType commandType, final NettyRequestProcessor processor, final ExecutorService executor) {
this.clientHandler.registerProcessor(commandType, processor, executor);
}
有两个共同点:
- handle 里都有
NettyEncoder NettyDecoder IdleStateHandler,因此可以实现一致的序列化、反序列化、心跳检测等 - handle 里分别有
NettyServerHandler、NettyClientHandler,两者又都支持了registerProcessor(...)方法。注册了哪些processor,就决定了可以以及如何处理哪些事件类型。
5. NettyRequestProcessor
以NettyServerHandler为例,该类继承自io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter,负责读写网络I/O数据。
通常我们关心的是channelRead方法(注意经过NettyDecoder handle 处理后,参数已经转为Command类型):
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
processReceived(ctx.channel(), (Command) msg);
}
然后调用processReceived处理:
private void processReceived(final Channel channel, final Command msg) {
final CommandType commandType = msg.getType();
if (CommandType.HEART_BEAT.equals(commandType)) {
...
}
final Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = processors.get(commandType);
if (pair != null) {
Runnable r = () -> {
try {
pair.getLeft().process(channel, msg);
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.error("process msg {} error", msg, ex);
}
};
try {
pair.getRight().submit(r);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
logger.warn("thread pool is full, discard msg {} from {}", msg, ChannelUtils.getRemoteAddress(channel));
}
} else {
logger.warn("commandType {} not support", commandType);
}
}
主要就是心跳包的处理,以及分发给合适的 processor 处理了。
6. 分发任务的RPC流程示例
6.1. Master
TaskPriorityQueueConsumer.dispatchTask创建了Command对象
protected boolean dispatchTask(TaskPriority taskPriority) {
TaskExecutionContext context = taskPriority.getTaskExecutionContext();
ExecutionContext executionContext =
new ExecutionContext(toCommand(context), ExecutorType.WORKER, context.getWorkerGroup(),
taskInstance);
private Command toCommand(TaskExecutionContext taskExecutionContext) {
// todo: we didn't set the host here, since right now we didn't need to retry this message.
TaskDispatchCommand requestCommand = new TaskDispatchCommand(taskExecutionContext,
masterConfig.getMasterAddress(),
taskExecutionContext.getHost(),
System.currentTimeMillis());
return requestCommand.convert2Command();
}
TaskDispatchCommand转为Command:
public Command convert2Command() {
Command command = new Command();
command.setType(CommandType.TASK_DISPATCH_REQUEST);
byte[] body = JSONUtils.toJsonByteArray(this);
command.setBody(body);
return command;
}
之后就是调用NettyRemotingClient发送数据到 worker
6.2. Worker
WorkerRpcServer注册了TASK_DISPATCH_REQUEST的 processor:
public class WorkerRpcServer implements Closeable {
public void start() {
...
this.nettyRemotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(serverConfig);
this.nettyRemotingServer.registerProcessor(CommandType.TASK_DISPATCH_REQUEST, taskDispatchProcessor);
按照前面的介绍,收到消息后会调用TaskDispatchProcessor.process方法:
public void process(Channel channel, Command command) {
// body 转化为 TaskDispatchCommand
TaskDispatchCommand taskDispatchCommand = JSONUtils.parseObject(command.getBody(), TaskDispatchCommand.class);
...
// 初始化 WorkerTaskExecuteRunnable ,开始 worker 的处理流程
WorkerDelayTaskExecuteRunnable workerTaskExecuteRunnable = WorkerTaskExecuteRunnableFactoryBuilder
.createWorkerDelayTaskExecuteRunnableFactory(
taskExecutionContext,
workerConfig,
workflowMasterAddress,
workerMessageSender,
alertClientService,
taskPluginManager,
storageOperate)
.createWorkerTaskExecuteRunnable();
// submit task to manager
boolean offer = workerManager.offer(workerTaskExecuteRunnable);
经过上述的 RPC 过程,待执行的任务实例信息就从 master 分发到了 worker,开始真正执行。
7. 总结
字节在模块间的流转过程,本质是这样的:
BaseCommand -> Command -> buf -> buf -> Command -> BaseCommand
Command是 RPC 通信的基础数据结构,BaseCommand封装了业务请求逻辑。
这些过程被封装了NettyRemotingServer NettyRemotingClient,上层通过注册 processor 的方式订阅对应的 Command 类型。在实现调度的核心逻辑时,就可以聚焦在具体的NettyRequestProcessor上,而无需关注底层网络模型了。