上篇笔记 skiplist 简介里从理论上介绍了 skiplist,本文对照 leveldb 的 C++ 源码看下 skiplist 的实现,同时介绍下 leveldb 里的实现技巧。
leveldb 在 MemTable 里使用 skiplist 高效的插入与查找数据。
typedef SkipList<const char*, KeyComparator> Table;
Table table_;
存储的数据类型为const char*,KeyComparator定义如下,主要起到比较 key 的作用:
struct KeyComparator {
const InternalKeyComparator comparator;
explicit KeyComparator(const InternalKeyComparator& c) : comparator(c) { }
int operator()(const char* a, const char* b) const;
};
1. SkipList 类简介
SkipList 是一个模板类
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
class SkipList
其中 Key 为要存储的数据类型,Comparator 实现 Key 的比较。
提供了两个接口Insert && Contains,即插入与查找,没有Delete接口。
// Insert key into the list.
// REQUIRES: nothing that compares equal to key is currently in the list.
void Insert(const Key& key);
// Returns true iff an entry that compares equal to key is in the list.
bool Contains(const Key& key) const;
包含以下几个成员变量
// Immutable after construction
Comparator const compare_;
//leveldb内存池
Arena* const arena_; // Arena used for allocations of nodes
Node* const head_;
// Modified only by Insert(). Read racily by readers, but stale
// values are ok.
port::AtomicPointer max_height_; // Height of the entire list
// Read/written only by Insert().
//随机数产生器
Random rnd_;
其中arena_是 leveldb 的内存池,用于分配节点内存,rand_是 leveldb 的随机数产生器,用于解决 skiplist 里”抛硬币”的问题。
max_height_记录当前最大高度,compare_用于 key 比较,head_即首节点。
先看下构造函数
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena)
: compare_(cmp),
arena_(arena),
head_(NewNode(0 /* any key will do */, kMaxHeight)),
max_height_(reinterpret_cast<void*>(1)),
rnd_(0xdeadbeef) {
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxHeight; i++) {
head_->SetNext(i, nullptr);
}
}
max_height_初始化为1,head_申请了内存并且初始化,其中enum { kMaxHeight = 12 };,也就是论文里的 MaxLevel.
2. Node && NewNode
前面看到head_通过NewNode构造出来,并且调用了SetNext函数,本节先分析下都是在做什么。
Node 对应 skiplist 里的节点,包含了 key 以及 若干层的后继节点地址。定义如下:
// Implementation details follow
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { }
Key const key;//数据本身
//获取或者设置该节点在第n层的后继节点
// Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
}
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].Release_Store(x);
}
// No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
}
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
}
private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
// 作为Node的最后一个成员变量
// 由于Node通过placement new的方式构造,因此next_实际上是一个不定长的数组
// 数组长度即该节点的高度
// next_记录了该节点在所有层的后继节点,0是最底层链表。
port::AtomicPointer next_[1];
};
所有的 Node 对象都通过NewNode构造出来:先通过arena_分配内存,然后通过 placement new 的方式调用 Node 的构造函数。
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::NewNode(const Key& key, int height) {
//额外存储(height - 1)个port::AtomicPointer
char* mem = arena_->AllocateAligned(
sizeof(Node) + sizeof(port::AtomicPointer) * (height - 1));
return new (mem) Node(key);
}
因此可以看到SkipList构造函数里初始化了head_,高度为kMaxHeight,并且设置每一层的后继节点为nullptr。
3. Insert && Contains
这里是 skiplist 比较核心的部分,不过 leveldb 实现上考虑了自身的使用场景,没有实现 delete。
3.1. Insert
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
//prev记录每一层最后一个 < key的节点,也就是待插入节点的前驱节点
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == nullptr || !Equal(key, x->key));
//随机决定节点高度height
int height = RandomHeight();
//如果新的高度比当前所有节点高度都大,那么填充prev更高层为head_,同时更新max_height_
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
//fprintf(stderr, "Change height from %d to %d\n", max_height_, height);
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (nullptr), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since nullptr sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast<void*>(height));
}
//构造Node,高度为height
x = NewNode(key, height);
//插入节点x到prev及prev->next中间
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
// 先修改x节点,再修改prev节点
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
RandomHeight就是通过抛硬币的方法随机决定该节点高度
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList<Key,Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
// 1/4概率继续增加height
while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == 0)) {
height++;
}
assert(height > 0);
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
}
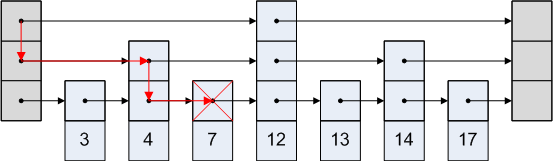
对比上篇笔记的search伪代码可以比较容易看懂FindGreaterOrEqual,注意这里是查找 >= 而不是 = .
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev)
const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {//如果next->key < key
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else {//如果next->key >= key
//notes:如果单纯为了判断是否相等,这里可以加一个判断直接返回了,没必>要level--到0再返回,不过复杂度没有变化
if (prev != nullptr) prev[level] = x;//prev记录该level最后一个<key的节点
if (level == 0) {//到达最底层则返回next (next是第一个>=key的节点)
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
}
}
}
3.2. Contains
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Contains(const Key& key) const {
//x记录第一个>= key的Node
//注意FindGreaterOrEqual是查找>=key的Node,因此会迭代直到level = 0才返回
//实际上可以实现一个接口直接查找==key的Node,这样会在level >=0 时就能返回,查找的时间复杂度不变,不过可以预期减少比较次数。
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, nullptr);
//判断x->key == key
if (x != nullptr && Equal(key, x->key)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
4. FindLast && FindLessThan
Contains Insert都用到了FindGreaterOrEqual,leveldb 还提供了:
FindLessThan查找最大一个< key的节点FindLast查找最后一个节点
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindLessThan(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;//获取当前最大height
while (true) {
assert(x == head_ || compare_(x->key, key) < 0);
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (next == nullptr || compare_(next->key, key) >= 0) {//如果key >= next->key
if (level == 0) {
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
} else {
x = next;
}
}
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindLast()
const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (next == nullptr) {//到达最后一个节点
if (level == 0) {//level=0,则返回
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
// level>0则到下一层
level--;
}
} else {
//不是最后一个节点则继续递增
x = next;
}
}
}
5. Iterator
MemTable在读取时使用的是SkipList::Iterator
定义如下:
// Iteration over the contents of a skip list
class Iterator {
public:
// Initialize an iterator over the specified list.
// The returned iterator is not valid.
explicit Iterator(const SkipList* list);
// Returns true iff the iterator is positioned at a valid node.
bool Valid() const;
// Returns the key at the current position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
const Key& key() const;
// Advances to the next position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
void Next();
// Advances to the previous position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
void Prev();
// Advance to the first entry with a key >= target
void Seek(const Key& target);
// Position at the first entry in list.
// Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
void SeekToFirst();
// Position at the last entry in list.
// Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
void SeekToLast();
private:
const SkipList* list_;
Node* node_;
// Intentionally copyable
};
接口实现都比较简单,有的是直接调用上面介绍的Findxxx系列接口,这里就不介绍了,相比操作容器本身,使用 iterator 总是一个好习惯,正如 stl 的算法参数基本都是以迭代器作为参数。
6. notes
- 之前介绍抛硬币的方法概率为1/2,这里使用的是1/4,结合
kBranching = 4和kMaxHeight = 12,不影响复杂度的情况下,可以最多支持4**11 = 4194304个节点,因此在百万节点左右,这么设置参数效果最优。 FindGreaterOrEqual用于查找第一个>= key的Node,因此需要一直level--到最底层 list. 我觉得如果要查找= key的Node的话,可以修改为查找到= key的 Node 后,不用level--直接返回当前 Node. 忽略这条,参考6的实现,也是没有判断= key,因为时间复杂度不变,但实现更简洁?- 对应的单测位于
skiplist_test.cc,特别是ConcurrentTest的设计,比算法本身还要细致,我是只看懂了一部分😭,写单测一直有障碍的可以参考下。 - 读写并发:读操作不会修改内部数据,因此多个reader不存在竞争,并发没有问题;多个读单个写操作也没有问题,因为采用了原子变量以及
memory order,以及Insert里执行语句的前后顺序;多个写操作之间存在竞争关系,需要锁控制。 - 重点说明下
Insert里设置max_height_前的那段注释,读线程可能读到旧的或者新的值,无论是哪种值,写线程都可能在更新SkipList,因为后面更新是从低往高更新,而读是从高往低读,所以当读到新的节点的时候,继续往下层,一定是能读到正确值的。 - 这个地址下有完成的 C 实现及论文,leveldb里的实现几乎完整参考了这里,建议看下。
- 实现上类似于这张图,from Skip lists are fascinating!